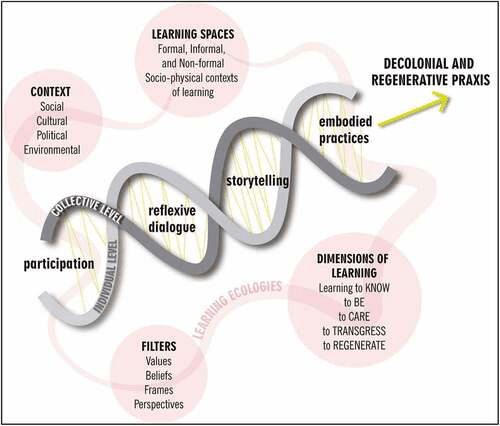
This collaborative multi-authored paper develops the methodological concept of river co-learning arenas (RCAs) and explores their potential to strengthen innovative grassroots river initiatives, enliven river commons, regenerate river ecologies, and foster greater socio-ecological justice. The integrity of river systems has been threatened in profound ways over the last century. Pollution, damming, canalisation, and water grabbing are some examples of pressures threatening the entwined lifeworlds of human and non-human communities that depend on riverine systems. Finding ways to reverse the trends of environmental degradation demands complex spatial–temporal, political, and institutional articulations across different levels of governance (from local to global) and among a plurality of actors who operate from diverse spheres of knowledge and systems of practice, and who have distinct capacities to affect decision-making. In this context, grassroots river initiatives worldwide use new multi-actor and multi-level dialogue arenas to develop proposals for river regeneration and promote social-ecological justice in opposition to dominant technocratic-hydraulic development strategies. This paper conceptualises these spaces of dialogue and action as RCAs and critically reflects on ways of organising and supporting RCAs while facilitating their cross-fertilisation in transdisciplinary practice. By integrating studies, debates, and theories from diverse disciplines, we generate multi-faceted insights and present cornerstones for the engagement with and/or enaction of RCAs. This encompasses five main themes central to RCAs: (1) River knowledge encounters and truth regimes, (2) transgressive co-learning, (3) confrontation and collaboration dynamics, (4) ongoing reflexivity, (5) transcultural knowledge assemblages and translocal bridging of rooted knowledge.
Citation:
De Souza, D. T., Hommes, L., Wals, A., Hoogesteger, J., Boelens, R., Duarte-Abadía, B., … Joy, K. J. (2024). River co-learning arenas: principles and practices for transdisciplinary knowledge co-creation and multi-scalar (inter)action. Local Environment, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/13549839.2024.2428215
The full paper can be downloaded here!